Last Updated: November 10th 2024

In alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 6, “Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all,” Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham established one of India’s most advanced and sustainable wastewater treatment ecosystems in 2024. This initiative directly contributes to Target 6.3.1, which aims to “improve water quality by reducing pollution, minimizing the release of hazardous chemicals, and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.” The system exemplifies Amrita’s deep commitment to environmental stewardship and its proactive efforts to create scalable, sustainable solutions for water conservation and reuse.
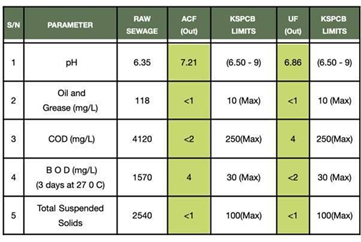
The University operates three decentralized Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs) across its campuses, with a combined treatment capacity of 1.4 million litres per day (MLD). These plants employ chemical-free biological processes, incorporating aerobic activated sludge treatment, sand and carbon filtration, and ultrafiltration (UF) systems. The result is high-quality recycled water that meets and often surpasses CPCB and SPCB discharge norms.

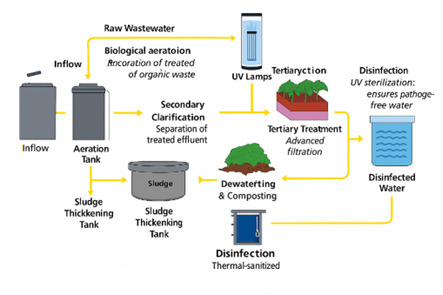
Each STP follows a multi-stage, zero-chemical, zero-liquid-discharge (ZLD) process:
The entire process is IoT-enabled, allowing real-time monitoring of pH, BOD, COD, TSS, and flow rates at every stage, ensuring regulatory compliance and operational transparency.

In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham reclaimed 688,200 cubic metres of treated wastewater — equal to 73% of the campus wastewater stream. Reconciling this figure implies a total treated/collected wastewater volume of approximately 942,740 m³ for the year. The reclaimed water is routed to non-potable on-campus applications such as:
Treated sludge rich in Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK) is composted and repurposed as organic fertilizer for the university’s extensive greenery and herbal gardens. This circular resource approach enhances soil fertility while minimizing waste.
Amrita integrates wastewater treatment with rainwater harvesting and greywater segregation as part of its Integrated Water Resource Plan (IWRP).
Ongoing innovations under the Amrita Live-in-Labs® initiative include:
A new 400 m³/day STP (STP IV) is planned for 2025–26 to further enhance capacity and serve expanding academic and residential facilities.
Together, these systems represent a model of campus-level circular water economy and position Amrita among the most environmentally responsible institutions in higher education.
Through its decentralized, data-driven, and sustainable wastewater management system, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham demonstrates complete alignment with SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation). Its ZLD policy, high reuse rate, nutrient recovery, and real-time monitoring together establish a replicable model for sustainable campus operations in India and beyond.