In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham actively informed and supported local, regional, and national governments in climate change disaster risk early warning and monitoring through sustained collaboration, scientific assessments, data integration, and deployment of advanced monitoring systems. These efforts focused on strengthening anticipatory action, evacuation planning, and risk-informed decision-making for climate-induced hazards such as landslides and tsunamis.
Following the severe landslide disaster in Mundakkai, Wayanad, in July 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, through its Centre for Wireless Networks and Applications (AWNA), conducted a joint field assessment with the Kerala State Disaster Management Authority (KSDMA). An eight-member expert team evaluated hazard conditions, exposure of settlements, and feasibility for deploying the Amrita Landslide Early Warning System A-LEWS.
The assessment directly supported government-led disaster risk monitoring by identifying priority zones for sensor deployment, early-warning-enabled evacuation planning, and reduction of future displacement risks under changing climatic conditions. As part of this cooperative response, Amma committed to funding the deployment of A-LEWS, strengthening long-term early-warning and monitoring capacity for the region.

Amrita continued its formal collaboration with the India Meteorological Department (IMD) under a Memorandum of Understanding on climate change risk assessment, modelling, and multi-hazard management. In 2024, IMD’s high-resolution meteorological datasets—particularly rainfall and atmospheric variables—were integrated into Amrita’s early-warning platforms. This data feeds directly into A-LEWS, which combines meteorological inputs with real-time monitoring of soil moisture, pore-water pressure, and geophysical parameters to support rainfall-threshold-based landslide risk monitoring. The integration enables state and district disaster management authorities to access scientifically informed insights for preparedness, monitoring, and anticipatory response.
At the coastal governance level, Amrita supported tsunami risk monitoring and early-warning preparedness by developing a Tsunami Evacuation and Shelter Map for Alappad Panchayat, Kerala, in collaboration with KSDMA and UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC).
The initiative combined geospatial hazard analysis, evacuation modelling, and direct community participation to produce an actionable tool for local authorities. The map supports early-warning response, evacuation routing, shelter planning, and displacement risk reduction, enabling the Panchayat and district authorities to operationalise tsunami preparedness within local administrative systems.

In December 2024, Amrita hosted the International Conference on Tsunami Risk Reduction and Community Resilience, convening NDMA India, KSDMA, INCOIS, UNESCO-IOC, and UNESCAP. The conference provided a structured platform for governments, scientists, and practitioners to exchange knowledge on early-warning systems, monitoring technologies, and climate-resilient disaster preparedness. Technical sessions, policy discussions, and a dedicated certificate programme on disaster resilience supported alignment between scientific monitoring capabilities and government disaster preparedness planning, strengthening cooperative approaches to climate risk management.


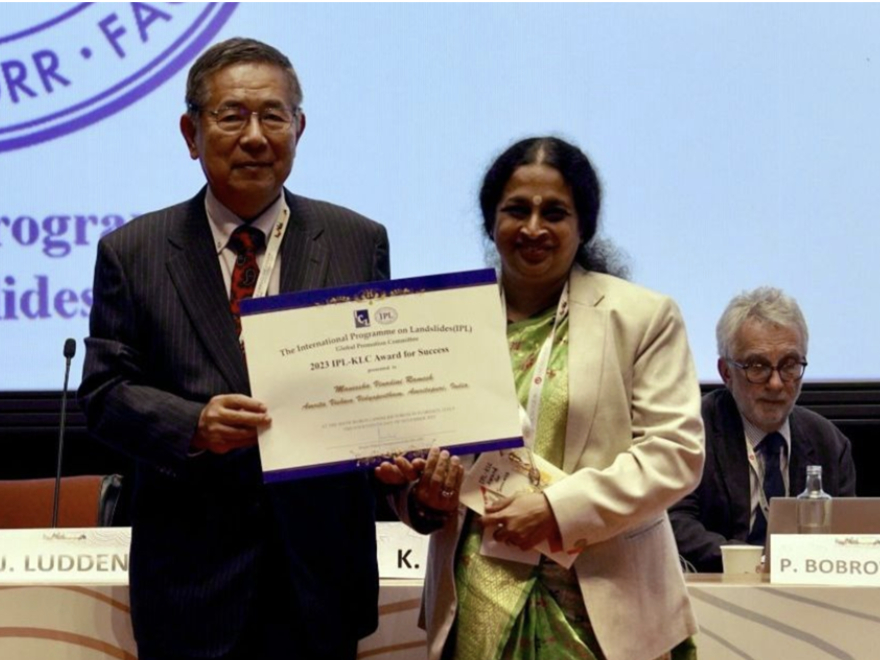
Amrita’s role in supporting government early-warning and monitoring is reinforced by its status as a World Centre of Excellence on Landslide Risk Reduction under the International Programme on Landslides, a designation valid through 2026. While re-conferred in 2023, this recognition remains operational in 2024 and reflects Amrita’s sustained contributions to early-warning science, monitoring systems, and government collaboration in climate-vulnerable regions.

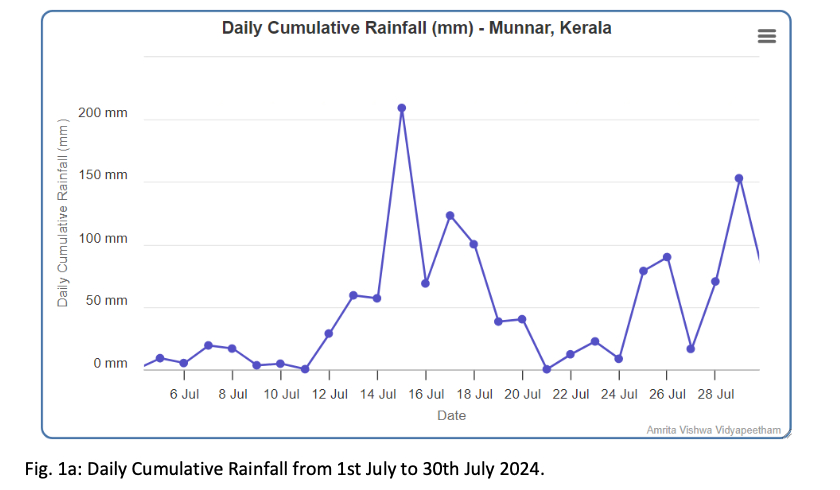
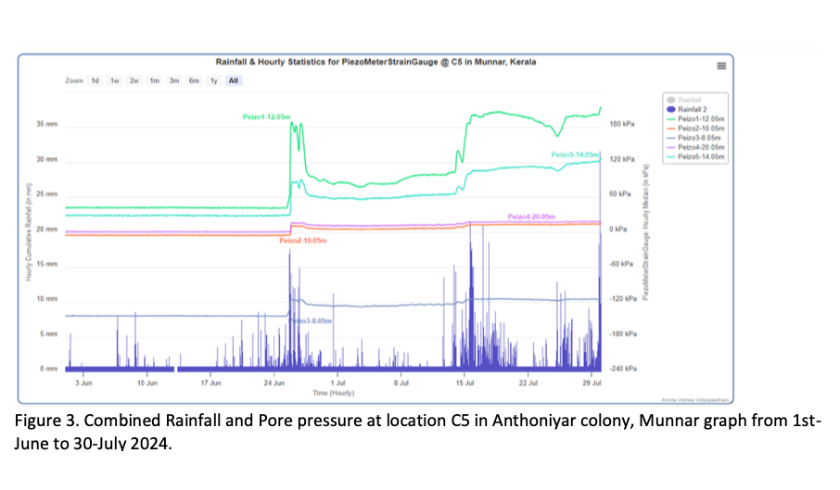
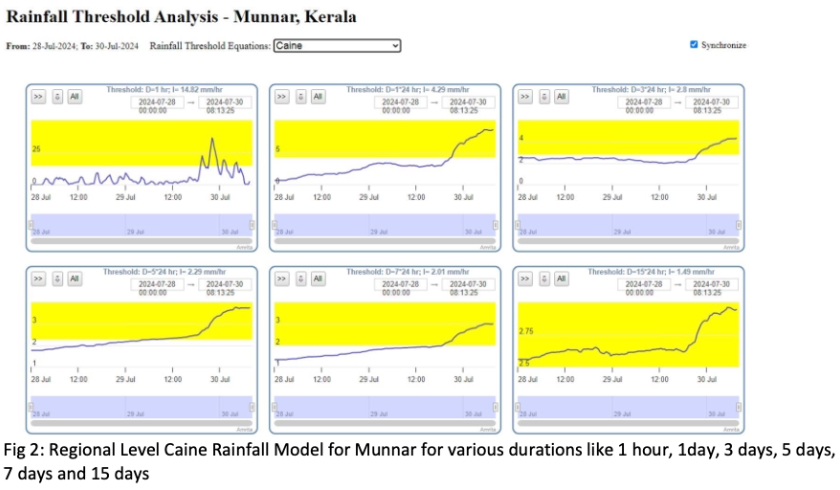
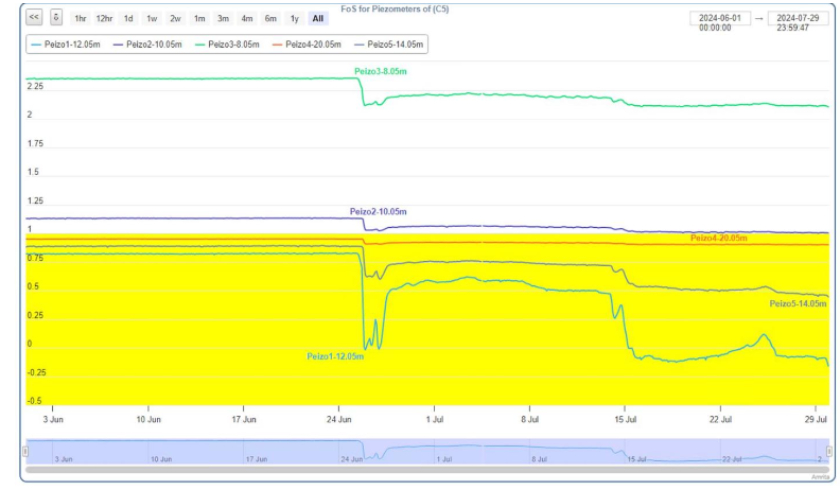
In June 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham actively informed and supported government authorities through its IoT-based Landslide Early Warning System (A-LEWS) deployed at Anthoniar Colony, Munnar, Idukki. The system, operational since 2009 with 150+ geological sensors and six Intelligent Wireless Probes recorded rainfall intensities and cumulative thresholds exceeding landslide-trigger levels, including 287.7 mm of rainfall over seven days and peak intensities of 51.6 mm/hour on 25 June 2024. Based on real-time monitoring, threshold analysis, and alignment with IMD’s heavy rainfall forecasts, Amrita formally notified authorities of the elevated risk of soil slips and landslidesacross vulnerable zones in the Munnar region, enabling early preparedness, monitoring, and risk-informed decision-making.