Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham demonstrates strong institutional commitment to sustainable water management through continuous monitoring, diversified sourcing, high levels of reuse, and infrastructure-led conservation across all campuses. In alignment with UN Sustainable Development Goal 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), the university operates an integrated, technology-enabled system for tracking water consumption, reuse, and source dependency, supporting data-driven governance and long-term water security.

Water consumption across academic, residential, healthcare, and utility facilities is monitored using a centralized digital platform supported by:
This system enables continuous visibility of water use patterns, early identification of leaks, and informed operational decision-making.
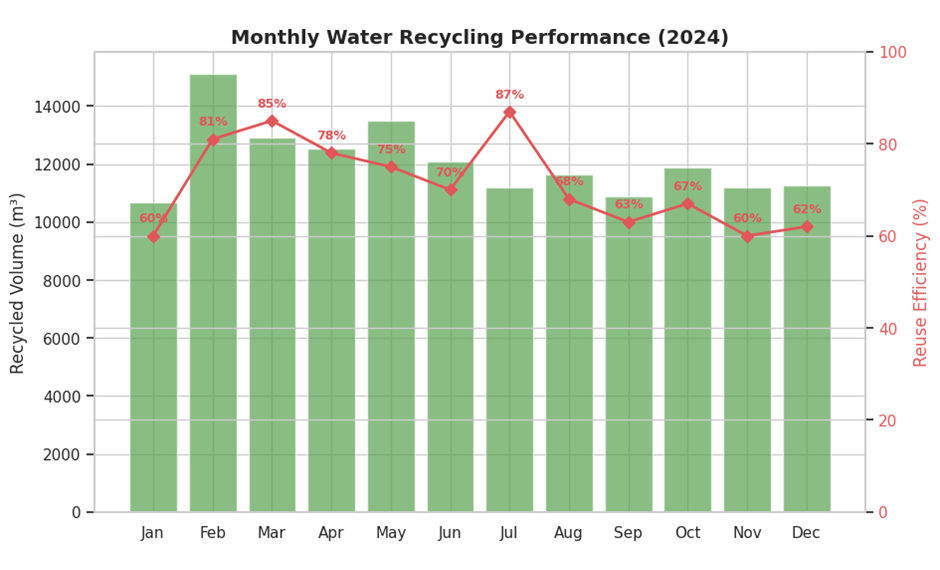
Over the past four years, Amrita has steadily strengthened its water management practices. Even as campus population and infrastructure have expanded, the university has consistently improved water reuse efficiency, reflecting effective governance, better monitoring, and sustained investment in reuse infrastructure.
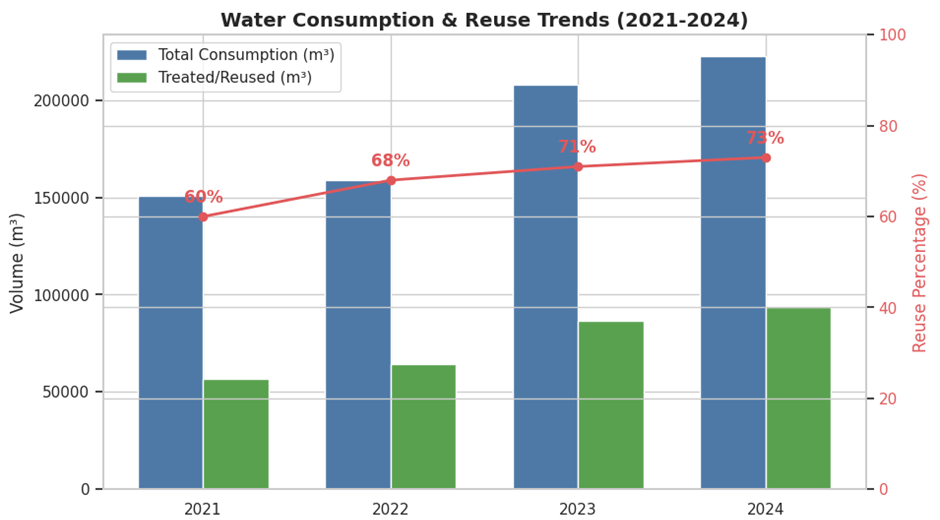
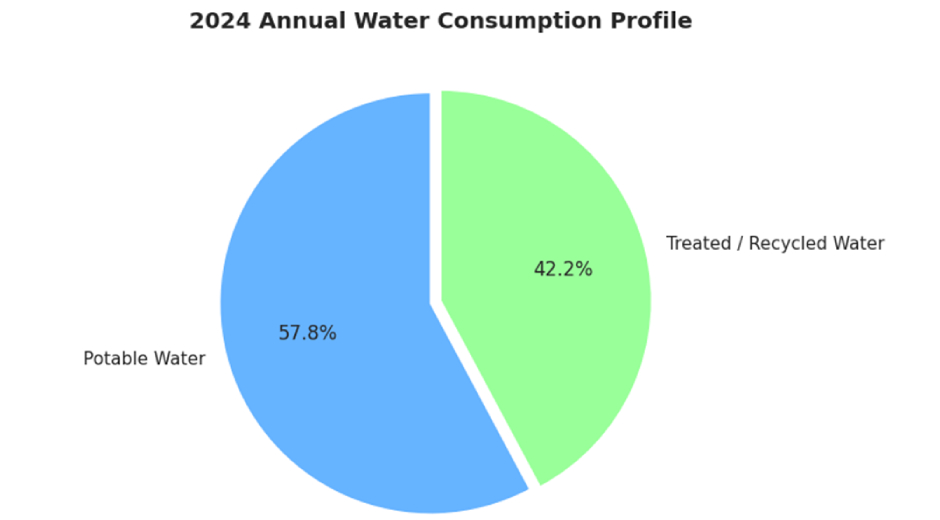
In 2024, Amrita recorded a total annual water consumption of 222,503 m³ across all campuses.
Treated and recycled water accounts for 42.2% of total water use, significantly reducing reliance on potable water sources. Recycled water is primarily used for toilet flushing, landscaping, irrigation, and other non-potable applications.
Despite serving a campus population of 38,930, per-capita water consumption remains well below the national benchmark of 135 litres per person per day, highlighting efficient water-use practices.
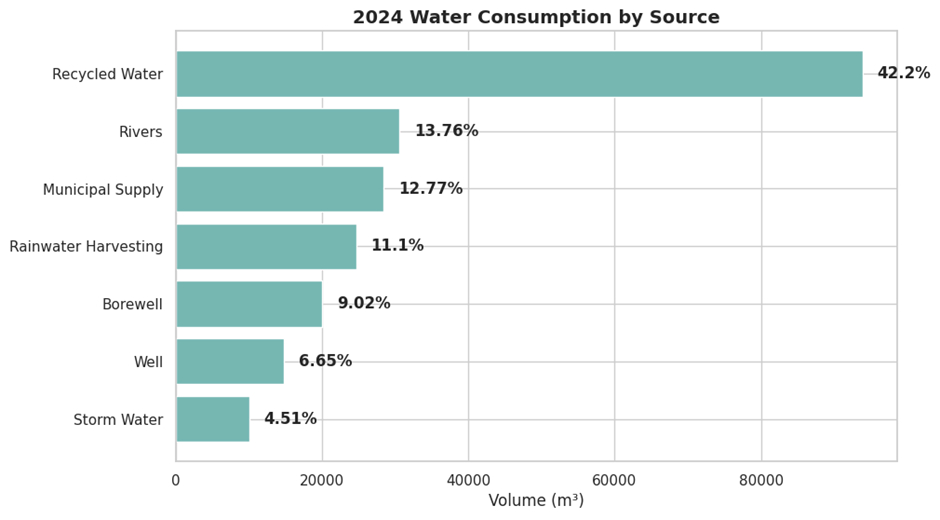
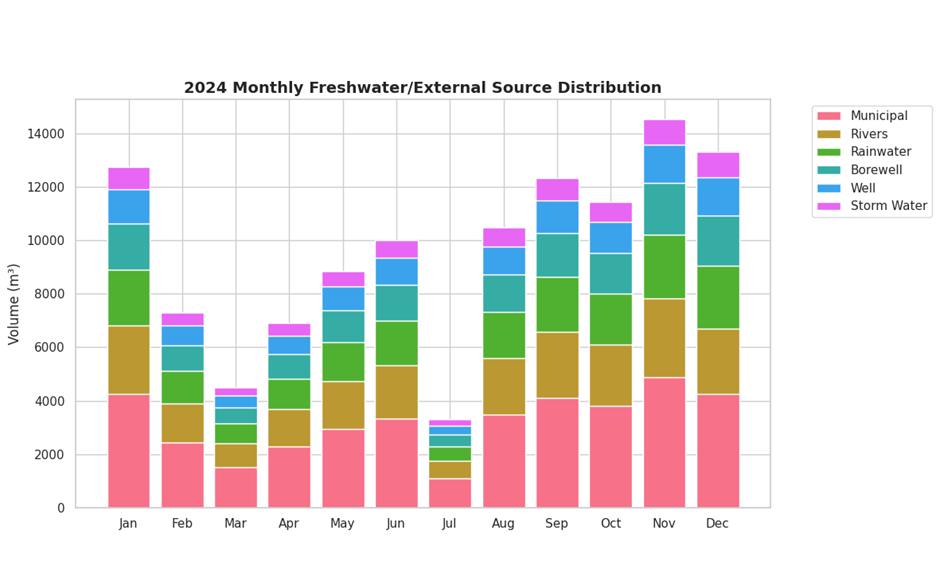
In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham’s total water consumption was met through a diversified sourcing mix, with treated and recycled water constituting the largest share at 42.2%, followed by surface water from rivers (13.76%), municipal mains supply (12.77%), rainwater harvesting systems (11.1%), borewells (9.02%), wells (6.65%), and stormwater capture (4.51%). This source-wise monitoring demonstrates comprehensive measurement of water drawn from mains supply, surface water bodies, groundwater sources, and recycled streams across the university.
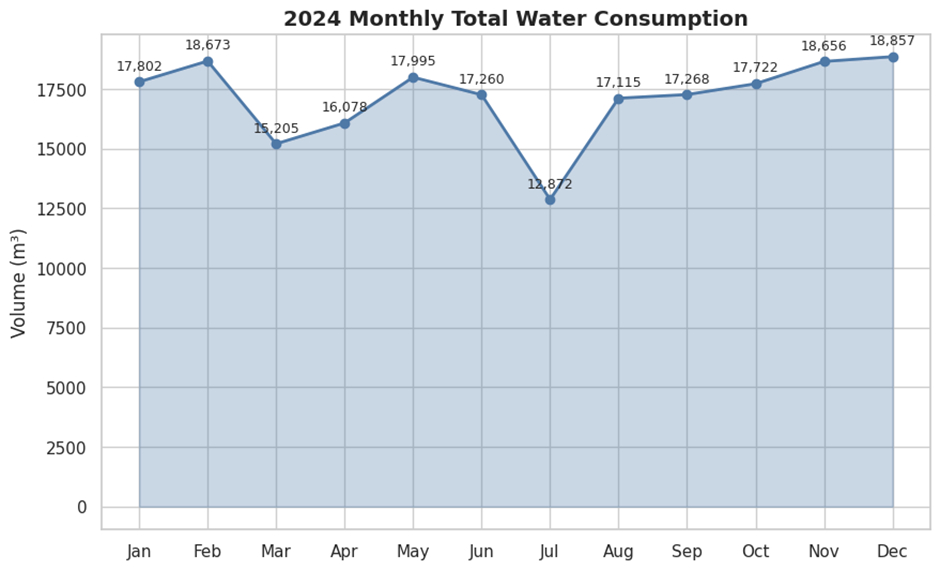
Water demand and availability vary across the year due to seasonal and climatic factors. Amrita adapts to these variations through flexible operational strategies, including increased use of treated wastewater and rainwater harvesting during periods of water stress.
This adaptive approach ensures consistent water availability while minimising environmental impact during both monsoon and non-monsoon periods.
Sustainable water management at Amrita is enabled by robust infrastructure and conservation initiatives, including:
All water consumption and reuse data are captured through digital meters and centralised monitoring systems. Monthly trends are derived from validated annual data using observed seasonal patterns. This ensures accuracy, transparency, and accountability in water reporting and management.
Through continuous monitoring, high levels of reuse, diversified sourcing, and conservation-focused infrastructure, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham actively contributes to SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation, promoting sustainable and resilient water management practices for the future.