Programs
- M. Tech. in Automotive Engineering -Postgraduate
- B. Sc. (Hons.) Biotechnology and Integrated Systems Biology -Undergraduate
Inspired by the Chancellor’s call to reduce carbon emissions, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham is committed to building a climate-positive, carbon-neutral future under its Sustainable Campus Policy. In 2023, the university launched a series of targeted initiatives to strengthen carbon management, enhance energy efficiency, and lower overall emissions. Through the adoption of sustainable operational practices and investment in innovative low-carbon technologies, Amrita continues to advance toward a more environmentally responsible and resilient campus ecosystem.
Highlights
Carbon Emission Control Measurement – Key Achievements
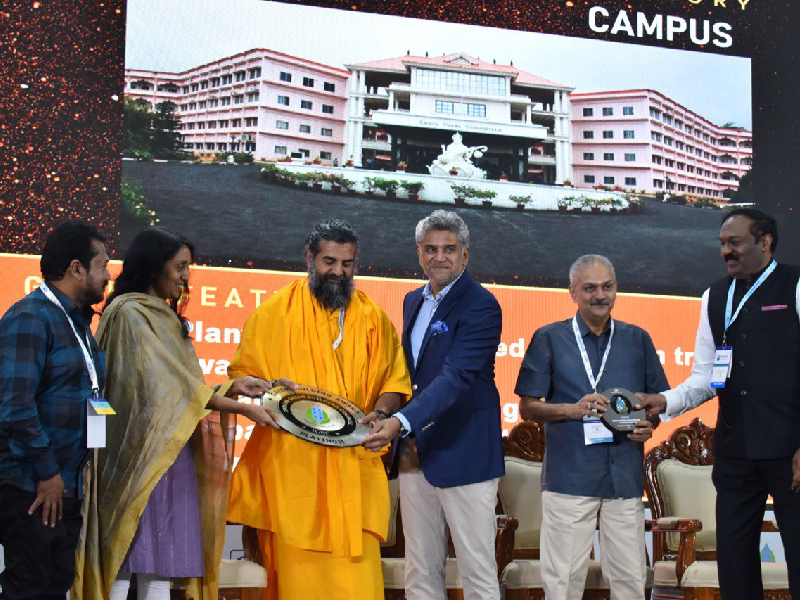

Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Coimbatore campus receiving an award related to green campus certification, highlighting its commitment to sustainability and carbon management.
On November 7, 2023, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham proudly announced its commitment to carbon neutrality by 2030 during the award ceremony where it received the coveted “Platinum” level certification under the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) Green Campus Rating System. This marks a significant milestone in the university’s journey toward creating a sustainable and eco-friendly educational environment.
The university has developed a comprehensive Net Zero Strategy document outlining its pathway to carbon neutrality, with a focus on reducing emissions across all three scopes through low carbon energy production. As the home to two UNESCO chairs and part of the C20 India 2023 initiative, Amrita has demonstrated global leadership in climate action.
The university has implemented a thorough, multi-faceted approach to carbon management and CO₂ emissions reduction:
Building Energy Monitoring and Management System
Amrita has implemented a real-time Building Energy Monitoring Dashboard that tracks and analyzes energy consumption across campus facilities. The system visualizes current usage, reviews historical trends, and calculates key indicators such as Energy Use Intensity (EUI) and Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE). It also monitors the building’s carbon footprint and provides automated alerts for abnormalities or inefficiencies.
Through remote access and control capabilities, facility managers can adjust system settings, optimize operations, and reduce unnecessary energy use. This monitoring process delivers annual energy savings of 379,200 kWh, equivalent to a reduction of 311 metric tons of CO₂ emissions per year, significantly improving the sustainability performance of campus buildings.
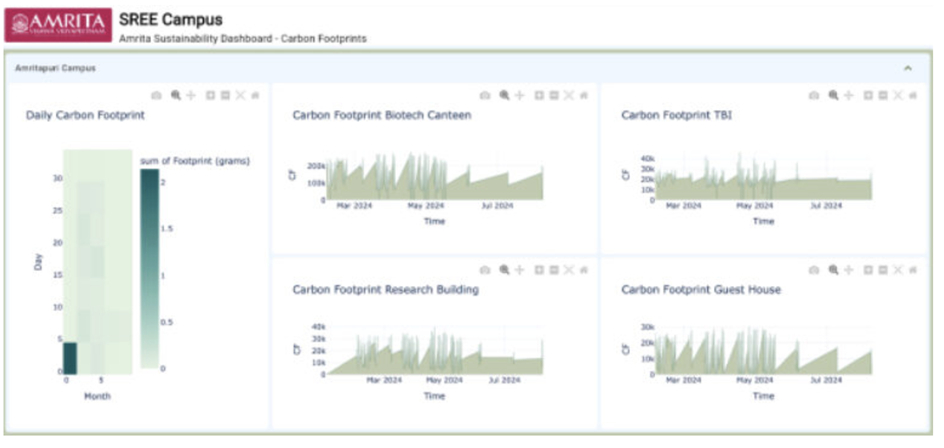
SREE Campus: Sustainability & Resilience Monitoring Dashboard
Amrita University has developed SREE (Sustainability & Resilience for Community Engagement & Empowerment) Campus, an advanced dashboard that monitors real-time sustainability performance across all campuses. The system tracks energy efficiency, climate conditions, and carbon emissions, providing live CO₂ data from electricity, heating, and cooling systems while enabling historical analysis to assess the impact of efficiency measures. SREE highlights the carbon intensity of different energy sources, supports low-carbon procurement decisions, and generates detailed emissions reports for compliance and sustainability reporting. By integrating data from multiple systems, the platform facilitates optimized resource management and informed decision-making.
Students also engage directly with sustainability insights, viewing real-time carbon-footprint data on building dashboards and campus TV screens.
Amrita University hallway showcasing LED lighting installations for energy efficiency across campus.
The university actively implements energy-efficient practices and technologies to reduce energy consumption and associated CO₂ emissions:
The university has achieved an impressive 30% reduction in grid dependency through its energy efficiency plan.

Sensor-Based Solar Lighting Systems
The campus has adopted sensor-based solar lighting systems across key outdoor areas, including pathways and parking zones. These lights operate entirely on solar energy and use advanced sensors to adjust brightness according to ambient light levels and detect motion, ensuring efficient energy use. By reducing dependence on grid electricity and minimizing light pollution, the system supports environmental conservation while delivering significant operational cost savings.
Smart Workspaces
Smart workspaces are designed to optimize energy consumption and enhance sustainability by integrating advanced technologies and innovative strategies. These spaces utilize intelligent building automation systems to control lighting, HVAC, and other systems based on occupancy and environmental conditions, reducing energy waste.
Additionally, energy-efficient lighting and appliances are employed to minimize power consumption. Smart workspaces often incorporate renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to further reduce reliance on traditional energy grids.
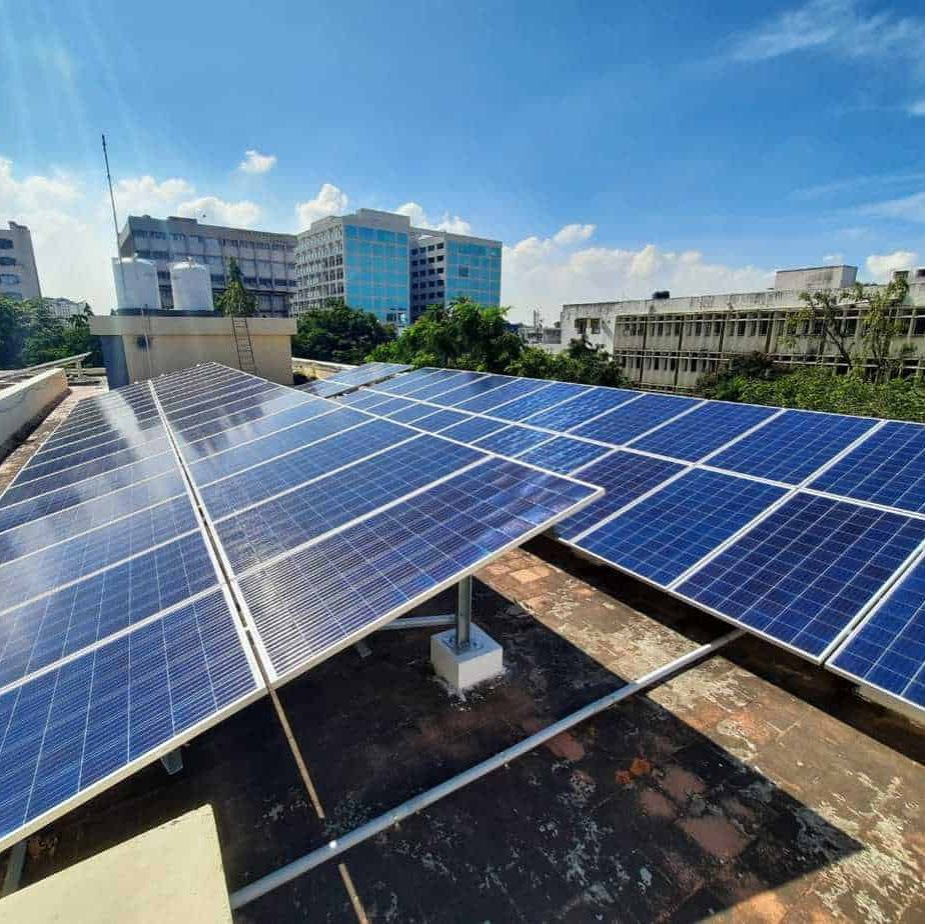
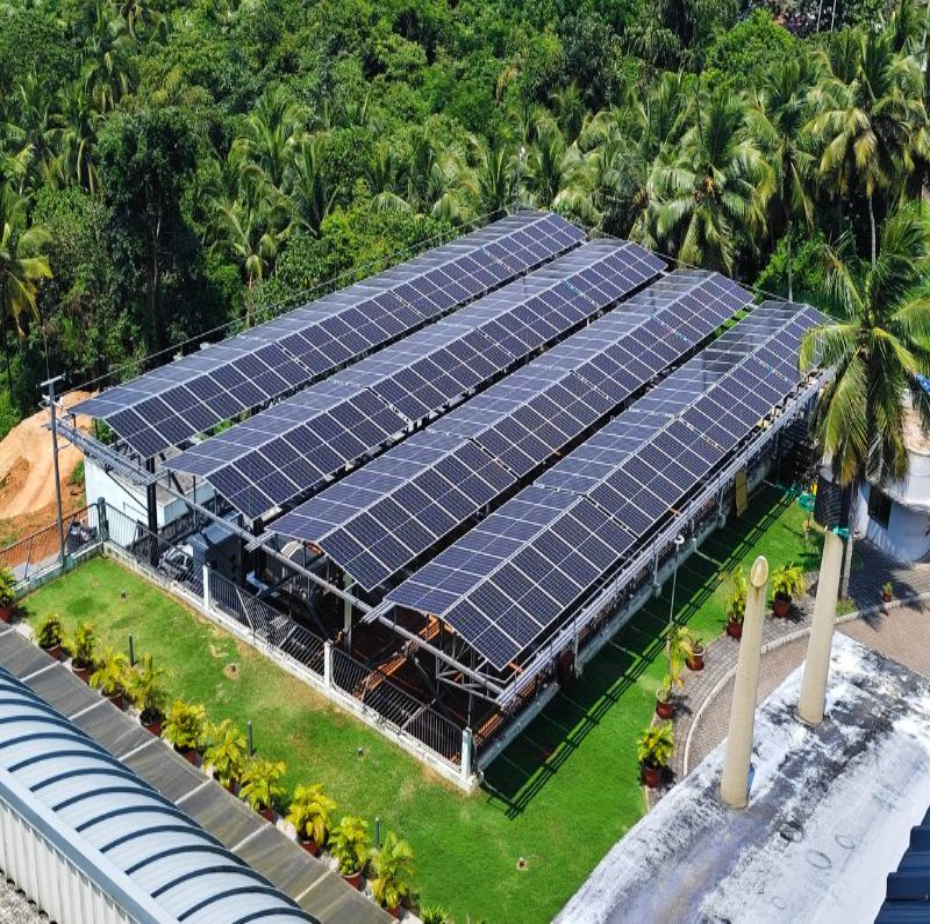



Amrita is determined to increase the use of renewable energy sources to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease CO₂ emissions:
Large academic buildings are equipped with 306 kWp of rooftop solar PV panels that harness solar power to generate substantial amounts of clean, renewable electricity, significantly reducing reliance on traditional energy sources.
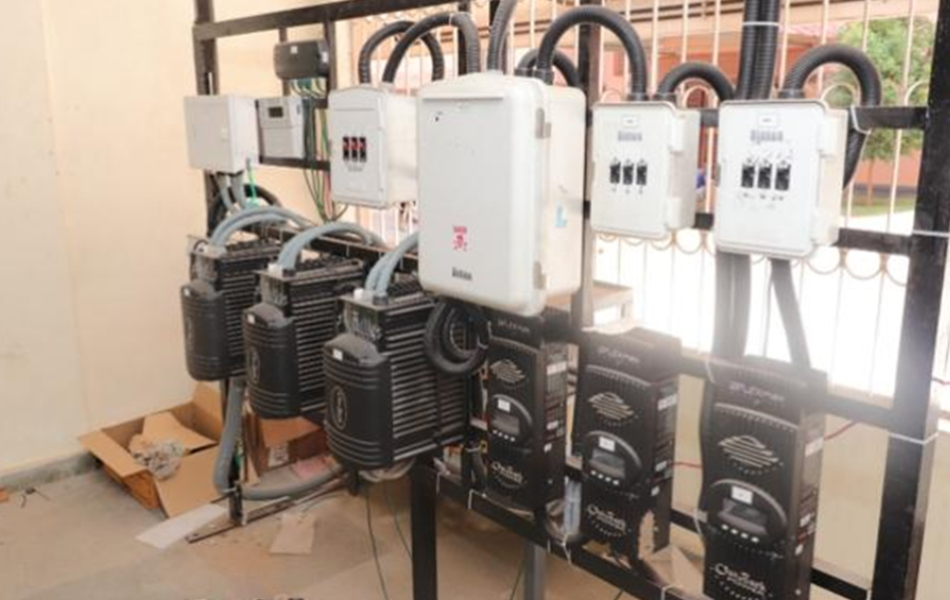

An inverter system plays a pivotal role in converting the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is compatible with our building’s electrical grid. This system is seamlessly integrated into our building monitoring system, allowing for real-time tracking of its performance. By monitoring key parameters such as inverter efficiency, temperature, and voltage, we can optimize its operation and ensure maximum energy output. Additionally, the integration enables early detection of potential issues, facilitating timely maintenance and minimizing downtime.


Four people carpooling in a car, illustrating sustainable transportation to reduce carbon emissions.

Electric vehicle charging station with reserved parking sign on a campus-like setting.
The university actively encourages sustainable transportation options to minimize carbon emissions from commuting and campus transportation:
Carpooling is heavily promoted within the campus, and the university has made significant investments in clean transportation technologies.

Outdoor waste bins labeled for compost, recycling, and landfill to support waste segregation and carbon management.
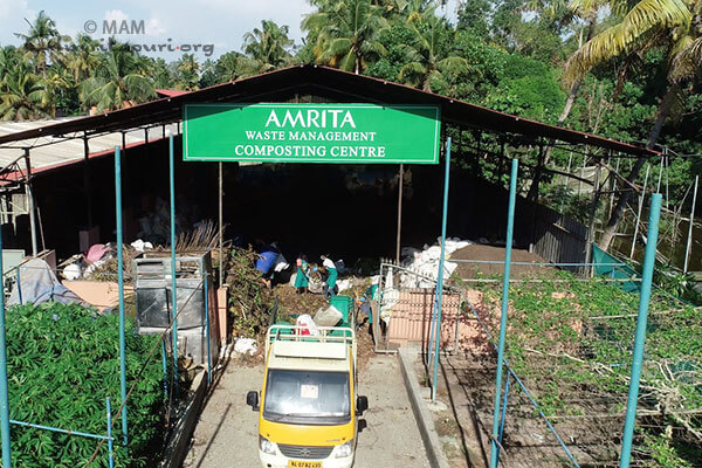

University students actively participating in recycling and composting waste on campus to manage carbon and reduce emissions.
Amrita has implemented effective waste management practices to minimize waste generation and promote recycling, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with waste disposal:re
The organic waste collected from Amala Bharatam Campaigns is used to create compost on campus, with food waste, dry leaves, and cow dung combined to produce rich compost in about 90 days. Research has shown that composting food waste instead of sending it to landfills can reduce emissions by the equivalent of up to 6 metric tons of carbon dioxide per metric dry ton of food waste.
Links:
The university prioritizes sustainable design principles in new construction projects and retrofits existing buildings:
Links:
Energy Efficient Thermal Comfort
The university enhances thermal comfort while minimizing energy consumption through high-performance building envelopes, efficient HVAC systems, and smart building technologies. Improved insulation, advanced glazing, and air-sealing reduce heat loss and gain, lowering heating and cooling demand. Energy-efficient HVAC units—equipped with variable-speed drives and high-efficiency components—further decrease energy use. Smart controls, including occupancy sensors and automated temperature adjustments, optimize system performance based on real-time conditions. Together, these measures create comfortable, low-energy indoor environments that support long-term sustainability goals.
Links:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
The university enhances thermal comfort while minimizing energy consumption through high-performance building envelopes, efficient HVAC systems, and smart building technologies. Improved insulation, advanced glazing, and air-sealing reduce heat loss and gain, lowering heating and cooling demand. Energy-efficient HVAC units—equipped with variable-speed drives and high-efficiency components—further decrease energy use. Smart controls, including occupancy sensors and automated temperature adjustments, optimize system performance based on real-time conditions. Together, these measures create comfortable, low-energy indoor environments that support long-term sustainability goals.
