Programs
- M. Tech. in Automotive Engineering -Postgraduate
- B. Sc. (Hons.) Biotechnology and Integrated Systems Biology -Undergraduate
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham undertakes systematic, university-wide measurement of low-carbon energy use across its campuses as part of its institutional commitment to climate action and sustainability. Energy consumption and low-carbon energy performance are tracked through a combination of university-level energy accounting, campus-level smart metering, and real-time digital dashboards, aligned with global best practices in higher-education climate reporting.
For global benchmarking and institutional reporting, Amrita reports the following metrics covering all campuses and all energy sources.
Operational low-carbon energy tracking is conducted through electricity-source data measured in kWh at campus level, including grid electricity, diesel-generated backup power, and on-site renewable energy. These measurements are supported by real-time monitoring systems that enable performance assessment, transparency, and data-driven decision-making.
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham undertakes institution-wide measurement of total energy consumption across all its campuses, covering academic buildings, hostels, laboratories, utilities, and shared infrastructure.
| Energy Category | Energy Use (GJ) |
| Total Energy Consumption (All Sources) | 244,800 GJ |
| Energy from Low-Carbon Sources | 136,221 GJ |
| Share of Low-Carbon Energy | 55.6% (~) |
This consolidated accounting represents all campuses and all energy sources and forms the basis for statutory reporting, global benchmarking, and strategic climate planning.
To support granular monitoring of the low-carbon transition, Amrita has implemented detailed source-wise electricity tracking at individual campuses using advanced metering and real-time monitoring systems. These campus-level datasets function as operational pilots and representative measurement units, informing university-wide renewable-energy expansion and decarbonisation strategies.
Electricity consumption at Amrita University is measured annually and disaggregated by energy source, including grid electricity, diesel-generated backup power, and on-site renewable energy (solar). Time-series data is maintained to track trends, efficiency improvements, and progress towards low-carbon energy use.
| Source of Electricity | Unit | 2021 (GJ) | 2022 (GJ) | 2023 (GJ) | 2024 (GJ ) |
| Grid Electricity (State Electricity Board) | GJ/year | 45,308 | 81,019 | 99,918 | 107,962 |
| Diesel Generator Power | GJ/year | 1,330 | 1,091 | 800 | 617 |
| Renewable Energy (Solar – Low Carbon) | GJ/year | 57,956 | 57,956 | 72,466 | 136,221 |
This campus-level dataset demonstrates a clear reduction in diesel-based electricity and a progressive increase in renewable energy generation, providing verified evidence of Amrita’s low-carbon energy transition in practice. Insights from such monitored campuses are used to inform scaling strategies across the wider university system.
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham has integrated on-site renewable energy, primarily solar, into campus operations and tracks renewable electricity generation quantitatively at each campus using smart metering and real-time monitoring systems.
These campus-level measurements serve as operational pilots and verified datasets that inform university-wide renewable-energy planning and scaling strategies. Campus-level renewable generation data is reported separately from consolidated university-wide energy consumption totals, ensuring transparency and methodological integrity in institutional reporting.
| Year | Installed Solar Capacity (kW) | CO₂ Emission Savings (kg) |
| 2023 | 250 | 312,485 |
| 2024 | 470 | 587,472 |
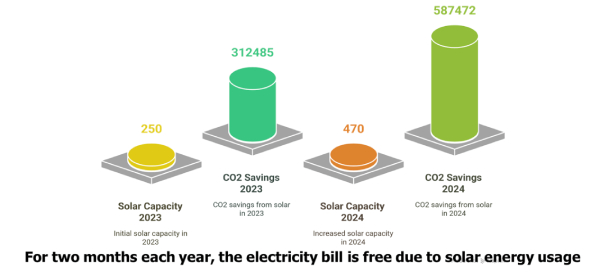
In addition to on-campus generation, Amrita has supported solar deployments in villages, schools, and community facilities, generating 19.7 lakh units of clean electricity. These community systems are clearly reported separately and are not included in institutional energy totals, ensuring transparency and methodological integrity.

At a monitored representative Amrita campus, diesel-generated electricity use is measured annually as part of operational low-carbon energy tracking.
Diesel electricity consumption at this campus declined from 1130 GJ (2021) to 617 GJ(2024), demonstrating a sustained reduction in reliance on carbon-intensive backup power.
This reduction reflects:
Baseline dependency on diesel-generated power at the monitored campus has been reduced through renewable-energy integration, daylight-optimised campus planning, and shared-space infrastructure, which collectively lower overall electricity demand.
The following cost-savings data relates to power-factor correction and efficient electrical distribution implemented at a monitored campus, and is reported as operational evidence of energy-efficiency outcomes, not as consolidated university-wide financial data.
| Year | Cost Saving (Rs / Year) |
| 2022 | 29,56,500 |
| 2023 | 36,95,625 |
| 2024 | 69,47,775 |
| Total (3 years) | 1,35,99,900 |
These savings demonstrate the financial and operational benefits of improved electrical distribution efficiency, complementing reductions in diesel use and supporting the campus-level low-carbon transition.
Low-carbon energy use and associated emissions reductions are tracked using Amrita’s SREE Campus Dashboard, an advanced sustainability monitoring platform that integrates:
At a monitored representative campus, solar energy deployment in 2024 resulted in over 5.87 lakh kg of CO₂ emissions avoided, with cumulative reductions increasing year-on-year. The dashboard supports transparent monitoring, operational optimisation, and institutional reporting, while also serving as a teaching and research tool for students and faculty.
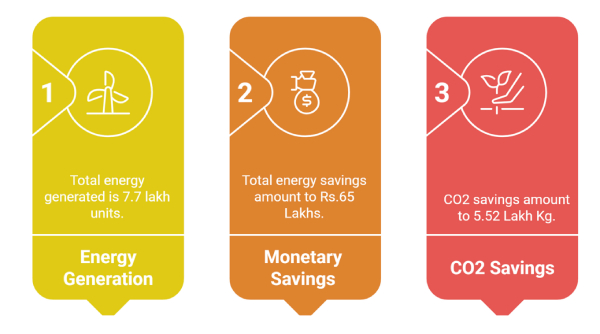
Through institution-wide measurement, quantified tracking of renewable energy, documented reduction in fossil-fuel use, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham demonstrates a comprehensive approach to measuring low-carbon energy use across the university. This integrated system supports informed decision-making, continuous improvement, and alignment with international best practices for climate action in higher education.
