In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham implemented and publicly shared its institution-wide Climate Action Plan, guiding coordinated action on climate mitigation, adaptation, resilience, and community engagement. The plan is actively shared and operationalised with local governments, municipal bodies, and community organisations, ensuring that climate strategies extend beyond the campus and support local and regional climate priorities.
Aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, Amrita’s Climate Action Plan integrates research, technology, education, and field-based engagement to support both campus decarbonisation and community resilience. The plan is designed for scaling, replication, and policy integration, enabling evidence-based climate action in partnership with public authorities and local communities.
Key Components of the Climate Action Plan (2024)
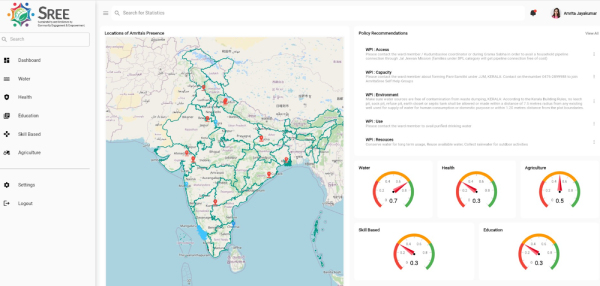
Data-Driven Climate Planning through the SREE Platform
Amrita continues to deploy and expand the SREE (Sustainability and Resilience for Community Engagement and Empowerment) platform as a core planning and decision-support tool under its Climate Action Plan. The platform enables:
The SREE platform has been applied across diverse geographic and socio-environmental contexts, supporting local governments, community organisations, and development stakeholders in planning climate-resilient interventions.
Real-Time Campus Carbon Footprint Monitoring
As part of its mitigation strategy, Amrita’s Climate Action Plan includes real-time carbon footprint tracking across campus infrastructure:
This system strengthens institutional accountability, supports data-driven emission reduction strategies, and serves as an educational tool for climate awareness and behavioural change.

Community-Centred Climate Action
A core pillar of Amrita’s Climate Action Plan is its community-first implementation approach, delivered through Live-in-Labs® and allied outreach programmes. In 2024, this included:

These initiatives ensure that climate action extends beyond campus boundaries and supports local adaptation and impact reduction.
Environmental Sustainability and Nature-Based Solutions
Amrita’s Climate Action Plan prioritises ecosystem-based approaches to climate adaptation and mitigation, including:
These actions link environmental protection directly to climate resilience and community well-being.

Net-Zero and Decarbonisation Pathways
Under its Climate Action Plan, Amrita advances long-term decarbonisation strategies, including:

These measures collectively support the university’s transition toward low-carbon and net-zero-aligned operations, while maintaining social and economic well-being.
Compassion-Driven Climate Governance
A distinctive element of Amrita’s Climate Action Plan is its emphasis on compassion-driven sustainability, integrating ethical considerations into climate education, governance, and action. Experiential learning models enable students and communities to connect climate solutions with local traditions, social equity, and lived realities, strengthening public acceptance and participation.

Sharing and Outreach
Amrita’s Climate Action Plan and associated initiatives are actively shared through:
This ensures transparency, public accessibility, and alignment with local and regional climate priorities.
A key feature of Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham’s Climate Action Plan is its formal sharing and co-implementation with local and state governments, ensuring that climate strategies translate into actionable outcomes for communities. Through long-term partnerships, Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs), and joint programmes, the university works closely with government agencies to strengthen climate resilience, early-warning systems, and adaptation planning.
Strategic Partnership with Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority (SSDMA)
Amrita maintains a long-standing collaboration with the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority (SSDMA), and is formalising a comprehensive Memorandum of Understanding to be signed in 2025, building on more than a decade of joint work in disaster risk reduction and climate resilience.
Under this partnership, Amrita’s Climate Action Plan is actively shared and implemented through:
This collaboration has evolved progressively, from early landslide-warning research to advanced multi-hazard systems addressing landslides, earthquakes, and flash floods. The integrated early-warning infrastructure enables real-time monitoring and advance alerts, supporting impact reduction and community safety across vulnerable regions.

Amrita has extended its climate adaptation and disaster preparedness initiatives to Odisha, working with the Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) and international partners. This collaboration focuses on early-warning deployment, institutional capacity building, and community training in landslide-prone regions.
Through this partnership, Amrita shares its climate-action expertise, technologies, and training frameworks with state authorities to strengthen disaster risk management systems and community preparedness.
Partnership with Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) for Landslide Early Warning and Climate-Risk Monitoring
In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham strengthened its regional disaster-risk collaboration through a formal partnership with the Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) to advance climate-related hazard monitoring and early-warning capabilities in landslide-prone districts of Odisha. The MoU builds on Amrita’s globally recognised expertise as a World Centre of Excellence on Landslide Risk Reduction and expands the deployment of the Amrita Landslide Early Warning System (A-LEWS) to the eastern region of India.
Through this collaboration, Amrita provides scientific, technological, and capacity-building support to OSDMA, enabling the state government to adopt evidence-based approaches to hazard anticipation, risk communication, and evacuation planning.

In 2024, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham shared and operationalised its Climate Action Plan with the Alappuzha Municipality, Kerala, through the Tsunami Ready Programme and “Wave of Change – A Month-long Water Sustainability Initiative” launched on World Water Day 2024. These initiatives addressed coastal risk preparedness, early-warning awareness, climate adaptation, and sustainable water management, through direct engagement with municipal leadership, ward-level governance structures, community training, and identification of local “water and resilience champions,” demonstrating integrated climate action at the municipal level.






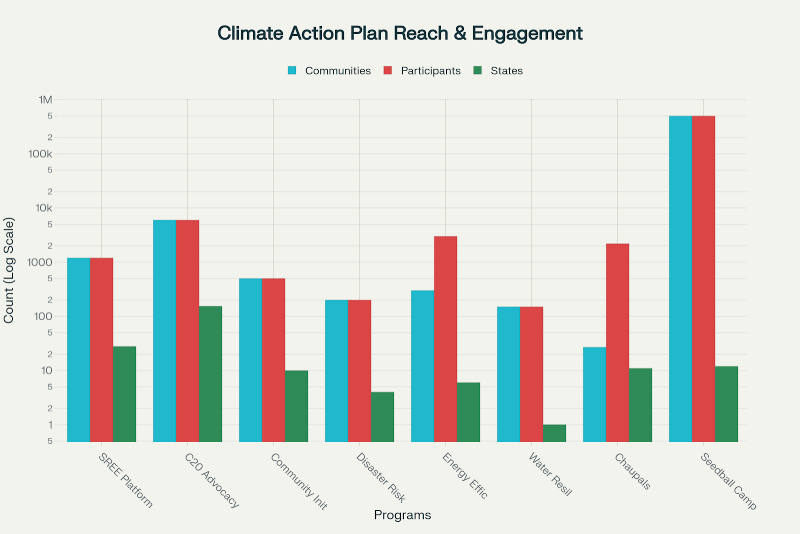
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham has developed and implemented a comprehensive Climate Action Plan that positions the university as a leader in climate resilience and sustainable development at local, national, and global scales. The plan integrates advanced technology, evidence-based research, policy advocacy, and grassroots community engagement, aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals and global commitments outlined at COP28. The Climate Action Plan is actively shared with local governments, state authorities, and community organizations, creating a collaborative framework for climate action across 1,200+ communities in 28 Indian states and 154 countries globally.
Official Climate Action Plan Documentation:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg-25/sdg13/climate-action-plan/
The SREE (Sustainability & Resilience for Community Engagement & Empowerment) Platform represents Amrita’s flagship technology solution for translating climate action into local practice. Launched at the International Conference on Sustainable & Resilient Futures (ICSRF 2025), SREE is a geo-spatial, crowd-sourced platform designed to empower rural communities with sustainability and resilience data.
Community Reach: 1,200+ communities across 28 Indian states, reaching government agencies and rural households
Link to SREE Platform News:
https://www.amrita.edu/news/sree-a-geo-spatial-platform-empowering-villages-for-sustainability-and-resilience/
As a leading example for communities, Amrita has installed real-time carbon monitoring dashboards in every campus building across its eight campuses. This transparent, live-tracking system creates climate awareness among students, faculty, and administrative staff.
Link to Campus Carbon Monitoring:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg-25/sdg13/low-carbon-energy-tracking/
Amrita hosted and led the Civil 20 India 2023 Working Group on Sustainable and Resilient Communities – Climate, Environment and Net Zero Targets, one of 16 working groups under C20 India. This critical initiative directly influenced G20 policy recommendations and global climate governance.
Global Recognition and Leadership Transition:
In 2024, Amrita Dean Prof. Krishnashree Achuthan represented India’s C20 leadership at the G20 closing summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil (November 13, 2024), continuing advocacy for climate resilience and adaptive policies.
C20 India 2023 Working Group Documentation:
https://c20.amma.org/src-wg/
Policy Development Page:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg/sdg7/policy-development-for-clean-energy-tech/
Amrita Dean’s G20 Representation (2024):
https://www.amrita.edu/news/amrita-dean-prof-krishnashree-represented-indias-c20-leadership-during-2024s-g20-event-at-brazil/
One of Amrita’s most significant climate action partnerships is with the Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority. A comprehensive Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed on May 10, 2025, formalizing over a decade of collaborative work in disaster risk reduction and climate resilience.
The AI-enabled landslide early warning system uses over 200 sensors to monitor:
Data flows from Field Management Centre (FMC) in Sikkim to Data Management Centre (DMC) at Amrita for analysis, enabling early warnings 24 hours before potential landslide events, reducing disaster impact by approximately 30%.
Official SSDMA Partnership Announcement:
https://www.amrita.edu/news/amrita-partners-with-sikkim-state-disaster-management-authority-strengthen-community-resilience-eastern-himalayas/
Government Support and Collaboration Documentation:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg-25/sdg13/colloborations/
Amrita has extended its landslide early warning and disaster preparedness initiatives to Odisha, collaborating with the Odisha State Disaster Management Authority (OSDMA) and international experts from the Resilient and Inclusive Sustainable Economic development (RISE) project.
External News Coverage:
https://www.newindianexpress.com/states/odisha/2024/Mar/07/osdma-collaborates-with-rimes-amrita-for-disaster-preparedness
The “Wave of Change: Water for a Sustainable Future” initiative demonstrates Amrita’s integration of climate adaptation with local government and municipal leadership.
Wave of Change Initiative Documentation:
https://www.amrita.edu/events/wave-of-change-water-for-a-sustainable-future/
News Article on Wave of Change Launch:
https://www.amrita.edu/news/wave-of-change-amrita-vishwa-vidyapeetham-launches-a-month-long-water-sustainability-initiative-on-world-water-day-2024/
The C-Chaupals represent Amrita’s methodology for ensuring inclusive, participatory climate action at the grassroots level. These initiatives brought together diverse community voices—villagers, local administration, Self Help Group members, farmers, women residents, and health workers—for collective climate and sustainability discussions.
C-Choupals operated as collective decision-making forums where community voices directly informed government and organizational policies, demonstrating participatory climate governance.
Launched under the C20 India 2023 Working Group, the Global Seedball Campaign represents unprecedented mobilization for climate action through ecosystem restoration.
Each seedball contained seeds, soil, and nutrients, designed for easy dispersal in fragile ecosystems. The campaign combined environmental education with direct restoration action, creating awareness about biodiversity conservation and climate impact reduction.
Dr. Krishnashree Achuthan highlighted the seedball campaign at the 2024 G20 closing summit in Brazil as a scalable, community-driven model for environmental sustainability.
Launched on World Water Day 2024, this month-long initiative coordinated climate adaptation with municipal and community structures.
Similar programs planned for 108 communities across India, creating a scalable model for water security in the context of climate change.
Amrita’s student-led energy efficiency campaigns extend climate mitigation education directly to villages surrounding all university campuses.
Detailed Program Information:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg/sdg7/amrita-vishwa-vidyapeetham-student-led-programs-on-energy-efficiency-and-clean-energy-in-villages/
Amrita’s climate action plan includes strategic partnerships with international and national NGOs for scaling environmental education impact.
Documentation of Environmental Education Collaborations:
https://www.amrita.edu/unsdg-25/sdg13/enviromental-education/
Amrita actively shares its Climate Action Plan findings and recommendations with government bodies at multiple levels through:
Global Climate Reports Recognition:
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham is highlighted in international climate reports as a model for integrating technology and community engagement for sustainability.
The university conducts regular community-level briefings on climate action plan components:
ARISE 2024 (Amrita Research & Innovation Symposium for Excellence) provided a platform for Amrita’s 500+ faculty members from eight campuses to collaboratively develop strategic research visions (1-year, 3-year, and 5-year) aligned with the climate action plan.
ARISE 2024 Documentation:
https://www.amrita.edu/events/arise-2024/
Through its UNESCO Chair on Experiential Learning for Sustainable Innovation and Development, Amrita has spearheaded development of a global curriculum on sustainable development applicable to 14 SDGs.
UNESCO Chair Documentation:
https://www.amrita.edu/unescochair-sustainable-development/

Amrita’s climate action plan specifically addresses water resilience through sustainable water governance frameworks and ecosystem restoration projects.
Link to Water Management Details:
https://www.amrita.edu/sustainable-water-management-pollution-prevention-2024/
Amrita’s Climate Action Plan operates through a network of formal partnerships:
| Partner Organization | Partnership Type | Focus Area | Geographic Scope |
| Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority | MoU (May 2025) | Disaster risk reduction, early warning | Sikkim, Northeast Himalayas |
| Odisha State Government | Collaboration Agreement | Disaster preparedness, landslide monitoring | Odisha state |
| Ministry of Earth Sciences (India) | Co-Funded Research | Landslide monitoring infrastructure | Pan-India |
| Alappuzha Municipality | Partnership Agreement | Water sustainability and community empowerment | Kerala |
| UNESCO Chair Network | Joint Implementation | SDG curriculum, sustainable innovation | Global (154 countries) |
| Civil 20 India | Hosted Working Group | Climate policy advocacy, net-zero targets | G20 nations |
| International Consortium on Landslides | Joint Training | Disaster resilience and capacity building | Multi-state |
| Team Environment Kenya | MoU-Based Collaboration | Environmental education and waste management | International |
The Climate Action Plan includes ambitious scaling targets:
Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham’s Climate Action Plan represents a comprehensive, multi-stakeholder approach to climate resilience that directly engages local governments, municipalities, civil society organizations, and communities. Through technology-enabled platforms, evidence-based research, inclusive policy advocacy, and grassroots implementation, the university demonstrates how educational institutions can catalyze systemic change toward sustainable and resilient communities across local, national, and global scales.